Table of Content
The greenhouse effect is a natural and vital process that makes life on Earth possible. It keeps our planet warm enough to sustain ecosystems, agriculture, and human civilizations. However, in recent decades, human activities have intensified the greenhouse effect, leading to global warming and climate change. This blog will explore what the greenhouse effect is, how it works, why its impact is increasing, the consequences of this change, and what we can do to mitigate it.
What Is the Greenhouse Effect?
The Basics of the Greenhouse Effect
The greenhouse effect occurs when gases in Earth’s atmosphere, like CO2, CH4, H2O, N2O, and O3, trap solar heat, preventing it from escaping into space. While water vapor is the most abundant, CO2 and methane are especially significant due to human-driven increases in their levels.
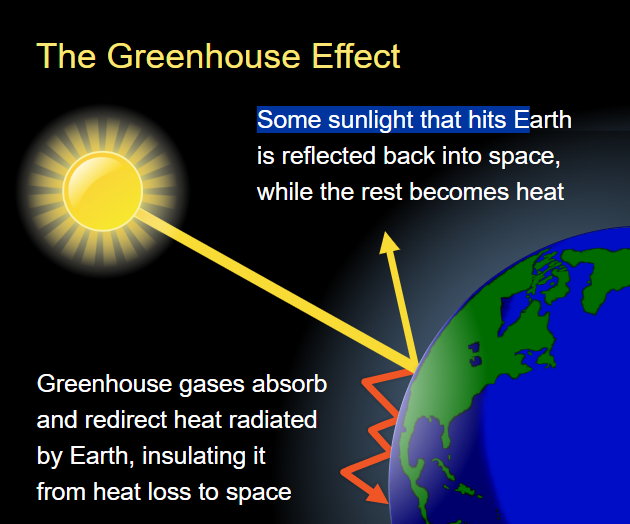
Here’s how the greenhouse effect works:
- Sunlight Reaches Earth: The sun emits energy in the form of sunlight, which travels through space and reaches Earth’s atmosphere. Some of this sunlight is reflected back into space by clouds, ice, and other reflective surfaces, but the majority passes through the atmosphere and reaches the Earth’s surface.
- Absorption and Heating: The Earth’s surface absorbs most of the sunlight, converting it into heat. This heat warms the land, oceans, and atmosphere, making the planet habitable.
- Heat Radiation: The Earth’s surface, in turn, radiates heat in the form of infrared energy. While some of this heat escapes into space, a significant portion is absorbed by greenhouse gases in the atmosphere.
- Heat Retention: Greenhouse gases trap this infrared radiation and re-radiate it in all directions, including back toward the Earth’s surface. This process keeps the planet warmer than it would be if all the heat escaped directly into space.
This natural greenhouse effect maintains the Earth’s average temperature at around 15°C (59°F). Without it, the planet would be an icy, uninhabitable world with an average temperature of about -18°C (0°F).
Why Is the Greenhouse Effect Intensifying?

Human Activities Driving the Enhanced Greenhouse Effect
While the greenhouse effect is essential for life, its intensification due to human activities is causing global temperatures to rise. This process is commonly known as the intensified greenhouse effect. The primary factors contributing to the enhanced greenhouse effect are:
- Burning Fossil Fuels
The burning of fossil fuels like coal, oil, and natural gas is the leading cause of increased greenhouse gas emissions. These fuels are used in power plants, vehicles, industries, and homes to generate energy. When burned, they release large amounts of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere, significantly boosting the greenhouse effect. - Deforestation
Forests play a crucial role in regulating the climate by absorbing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere through photosynthesis. However, deforestation—primarily for agriculture, logging, and urban development—reduces the number of trees available to absorb CO2. This leads to higher concentrations of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere, further intensifying the greenhouse effect. - Agricultural Practices
Modern agricultural practices contribute to the enhanced greenhouse effect in several ways. Livestock, such as cows and sheep, produce methane during digestion, a potent greenhouse gas. Additionally, the use of synthetic fertilizers in farming releases nitrous oxide, another powerful GHG. These activities add significant amounts of methane and nitrous oxide to the atmosphere, amplifying the greenhouse effect. - Industrial Processes
Certain industrial processes, such as cement production and the manufacture of chemicals, release various greenhouse gases into the atmosphere. These industries contribute to the increasing concentrations of carbon dioxide, methane, and other GHGs, enhancing the greenhouse effect. - Waste Management
Landfills are a major source of methane emissions. Organic waste, such as food scraps and yard waste, decomposes anaerobically in landfills, producing methane. Poor waste management practices lead to large amounts of this potent greenhouse gas being released into the atmosphere, contributing to global warming.
The Impacts of the Enhanced Greenhouse Effect
Rising Global Temperatures
A major consequence of the enhanced greenhouse effect is the increase in global temperatures. Over the past century, the Earth’s average temperature has increased by about 1.2°C (2.2°F). While this may seem like a small change, even a slight increase in temperature can have profound impacts on the planet’s climate.
Warmer temperatures are linked to more frequent and severe heatwaves, which can lead to droughts, wildfires, and heat-related illnesses. Higher temperatures also increase the evaporation rate, which can reduce water supplies and exacerbate drought conditions.
Melting Ice and Rising Sea Levels
The enhanced greenhouse effect is causing polar ice caps and glaciers to melt at an accelerated rate. As ice melts, it contributes to rising sea levels, which can lead to the flooding of coastal areas and the displacement of millions of people. Rising sea levels also threaten freshwater supplies by increasing the salinity of coastal aquifers.
The loss of ice also reduces the Earth’s albedo, or its ability to reflect sunlight. Ice and snow are highly reflective, so when they melt, darker ocean and land surfaces are exposed, absorbing more heat and further accelerating global warming.
Extreme Weather Events
Climate change driven by the enhanced greenhouse effect is making extreme weather events more frequent and severe. Hurricanes, typhoons, and cyclones are becoming more intense due to warmer ocean temperatures, which provide more energy for these storms. Similarly, warmer temperatures can lead to more intense and prolonged droughts in some regions, while others may experience increased rainfall and flooding.
These extreme weather events have devastating effects on communities, economies, and ecosystems. They can lead to loss of life, destruction of infrastructure, and disruptions to food and water supplies.
Disruption of Ecosystems
As global temperatures rise, many species struggle to adapt to the changing climate. Some may migrate to cooler areas, but not all species have the ability to move or find suitable habitats. This can lead to a loss of biodiversity as plants and animals that cannot adapt to the new conditions face extinction.
Marine ecosystems are also under threat due to the enhanced greenhouse effect. Warmer ocean temperatures are causing coral reefs to bleach and die, while the increased absorption of carbon dioxide by the oceans is leading to ocean acidification, which can harm marine life, especially shell-forming organisms.
Human Health Impacts
The enhanced greenhouse effect and the resulting climate change have direct and indirect impacts on human health. Increased temperatures can lead to heat-related illnesses, such as heatstroke and dehydration, particularly among vulnerable populations like the elderly and children.
Climate change can also affect the spread of infectious diseases. Warmer temperatures can expand the range of disease-carrying insects, such as mosquitoes, leading to the spread of diseases like malaria and dengue fever to new areas.
Additionally, extreme weather events can disrupt healthcare services and infrastructure, making it more difficult to respond to health emergencies.
What Can We Do to Mitigate the Greenhouse Effect?
Transition to Renewable Energy
One of the most effective ways to reduce the enhanced greenhouse effect is to transition away from fossil fuels and adopt renewable energy sources, such as solar, wind, and hydropower. These energy sources produce little to no greenhouse gas emissions, making them a key part of the solution to climate change.
Investing in renewable energy infrastructure, such as solar panels, wind turbines, and energy storage systems, can help reduce our reliance on fossil fuels and lower greenhouse gas emissions. Governments and businesses can also play a role by providing incentives for renewable energy adoption and investing in research and development of new clean energy technologies.
Increase Energy Efficiency
Improving energy efficiency is another important strategy for reducing the greenhouse effect. By using energy more efficiently, we can reduce the amount of energy we need to generate, which in turn reduces greenhouse gas emissions.
Energy efficiency can be improved in many ways, including upgrading to energy-efficient appliances, improving insulation in buildings, and adopting energy-saving practices, such as using public transportation or carpooling instead of driving alone.
Protect and Restore Forests
Protecting and restoring forests is a critical strategy for mitigating the enhanced greenhouse effect. Forests absorb CO2 from the atmosphere and store it in trees and soil. By preventing deforestation and promoting reforestation, we can help reduce the amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere.
Governments, businesses, and individuals can all play a role in protecting and restoring forests. This can include supporting policies that protect forests, participating in reforestation projects, and choosing products that are sustainably sourced and do not contribute to deforestation.
Adopt Sustainable Agriculture Practices
Sustainable agriculture practices can help reduce greenhouse gas emissions from farming. This can include reducing the use of synthetic fertilizers, adopting crop rotation and cover cropping, and improving livestock management to reduce methane emissions.
Supporting local and sustainable food systems can also help reduce the carbon footprint of food production. By choosing to buy locally grown and organic food, we can reduce the need for transportation and chemical inputs, which contribute to greenhouse gas emissions.
Support Climate Policies
Effective climate policies are essential for addressing the enhanced greenhouse effect and reducing greenhouse gas emissions. Governments can implement policies that set emission reduction targets, promote renewable energy, protect forests, and encourage sustainable agriculture.
Individuals can support climate policies by advocating for strong climate action at the local, national, and international levels. This can include voting for leaders who prioritize climate action, participating in climate advocacy groups, and raising awareness about the importance of addressing the greenhouse effect.
Raise Awareness and Educate Others
Raising awareness and educating others about the enhanced greenhouse effect and its impacts is crucial for driving action on climate change. By sharing information about the causes and consequences of the greenhouse effect, we can inspire others to take action and make more sustainable choices.
Education can take many forms, from talking to friends and family about climate change to participating in community events and campaigns. Schools, businesses, and organizations can also play a role by providing education and resources on the greenhouse effect and climate change.
Conclusion
The greenhouse effect is crucial for life on Earth, but human activities have intensified it, leading to global warming and climate change. This enhanced effect results in higher temperatures, melting ice, extreme weather, and disruptions to ecosystems and health. To combat this, we must work together globally and individually by using renewable energy, improving efficiency, protecting forests, practicing sustainable agriculture, supporting climate policies, and raising awareness. Every effort helps in addressing climate change.
Leave a Reply