Table of Content
If your web pages or blog posts are not indexed by Google, you’re not alone. It can be frustrating to see your content disappear from search results after putting in hard work to optimize it. Fortunately, with the right approach, you can troubleshoot and resolve these issues, regain visibility, and boost your SEO performance. Here’s a detailed guide to help you fix pages not indexed by Google.
Fix Pages Not Indexed by Google | Step by Step Guide –
Step 1: Identify Pages Not Indexed by Google in Google Search Console
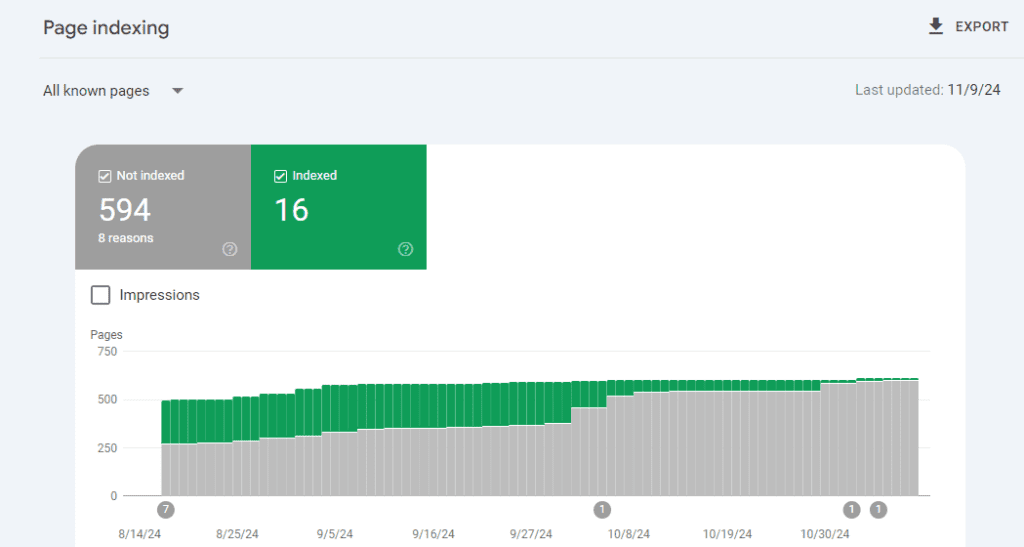
-
Log In to Google Search Console
- Head over to Google Search Console, log in with your Google account, and pick the website you want to check from the list.
-
Find Indexed and Non-Indexed Pages
- Once you’re in, look on the left side menu and click on Indexing > Pages. This is where you can see which pages Google has indexed (meaning they’re appearing in search results) and which ones haven’t made it yet.
-
See Why Pages Aren’t Indexed
- Google gives you reasons for why some pages haven’t been indexed. For example:
- 404 Errors: These are broken links where the page doesn’t exist.
- Duplicate Pages: Google might find multiple similar pages and skip indexing duplicates if they don’t have a clear “canonical” tag (a tag that tells Google which version to index).
- Noindex Tags: Sometimes pages are set to be hidden from search engines on purpose with a noindex tag.
- Redirects: If a page redirects to another URL, Google may skip indexing it directly.
- Other Errors: Other 4xx errors, like 403 (forbidden access), can block Google from reaching the page.
- Crawled but Not Indexed: Sometimes Google crawls a page but decides not to index it just yet.
- Discovered but Not Crawled: Google found the page but hasn’t actually crawled it.
- Google gives you reasons for why some pages haven’t been indexed. For example:
-
Review and Fix Any Issues
- For each reason, Google shows you the specific URLs affected so you know what to work on. Checking these reports regularly lets you catch issues early and improve your site’s chances of appearing in Google’s search results.
Step 2: Check for Manual Actions or Security Issues
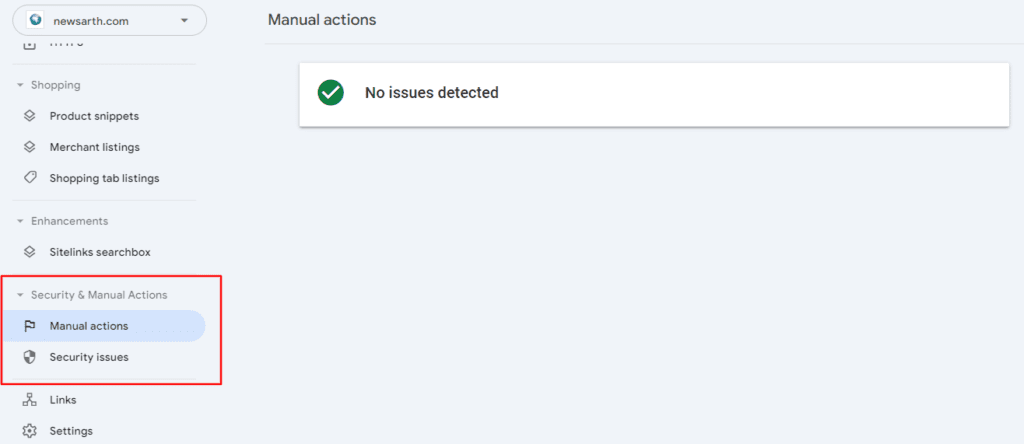
Google may deindex your pages if they detect manual actions or security issues on your site. Here’s how to check:
- Access the “Security & Manual Actions” Section: Go to Google Search Console and check the “Security & Manual Actions” section in the left sidebar.
- Review Manual Actions: Manual actions can occur if Google detects tactics aimed at manipulating rankings, such as using spammy or auto generated content. If you see any manual actions listed, it’s essential to address the underlying issue before requesting a review.
- Check for Security Issues: If your site was compromised, Google might deindex your pages due to security concerns. A hacked site can trigger a security warning. If you’ve been compromised, address the issue and request a security review to get your pages reindexed.
Addressing manual actions or security issues is crucial before you proceed with fixing other problems.
Step 3: Analyze Possible Causes of Deindexing
There are several content-related issues that can lead to pages not being indexed by Google. Here’s what to check:
- Content Quality and Uniqueness: Google prioritizes high-quality, original content. Pages with low-quality or thin content are more likely to be deindexed. Ensure your content is comprehensive, unique, and offers real value to users. For example, instead of writing short 300-word articles, aim to provide in-depth, detailed content that fully answers users’ queries.
- Update Outdated Content: Outdated pages may be deindexed, as Google prefers fresh, relevant content. Regularly update your posts, especially if they cover rapidly changing topics. For instance, if you wrote an article on “SEO Trends in 2020,” update it to reflect the latest 2024 trends to ensure it remains indexed.
- Check for Duplicate Content: Duplicate content can confuse Google’s crawlers. If you have similar pages across your site, use canonical tags to indicate which version should be indexed.
Addressing these content issues ensures that your pages are valuable and relevant, improving your chances of staying indexed.
Step 4: Core Web Vitals – Optimize for User Experience
Google places a high value on fast, user-friendly websites. Core Web Vitals are metrics that help you measure your site’s performance. Here’s how to check:
- Navigate to Core Web Vitals: In Google Search Console, go to the “Core Web Vitals” section to review your site’s mobile and desktop performance.
- Improve Slow Pages: Slow-loading pages can lead to poor user experience and may be deprioritized in search rankings. Use tools like Google’s PageSpeed Insights to analyze page speed and identify areas for improvement, such as optimizing images, reducing server response time, and leveraging browser caching.
- Monitor for “Poor” Pages: If any pages are flagged as “poor” in Core Web Vitals, prioritize improving their speed. Faster pages lead to better user experience and a higher chance of staying indexed.
Step 5: Verify Noindex Tags and Robots.txt
Technical issues can prevent Google from indexing your content. Here’s how to ensure your pages are not blocked from indexing:
- Ensure ‘Noindex’ Isn’t Applied: Sometimes, pages are mistakenly tagged with a “noindex” meta tag, which tells Google not to index them. You can use the “Inspect URL” tool in Google Search Console to check the status of specific pages.
- Check Robots.txt File: The robots.txt file controls which pages Google’s bots can crawl. If your important pages are blocked, they won’t be indexed. Double-check the robots.txt file to ensure it isn’t blocking any critical pages that should be indexed.
Step 6: Strengthen Internal Linking
Internal links help Google understand the structure of your site and identify which pages are the most important. Here’s how to improve internal linking:
- Increase Internal Links to Deindexed Pages: Link to affected pages from high-authority pages on your site to signal to Google that these pages are important.
- Use Descriptive Anchor Text: When creating internal links, use relevant keywords in the anchor text. This helps Google understand the topic of the linked page and boosts its relevance for indexing.
Step 7: Submit URL for Reindexing
Once you’ve addressed the issues causing pages not to be indexed by Google, you can request reindexing:
- Manual Re-indexing: In Google Search Console, use the URL Inspection Tool to submit a page for reindexing. This speeds up the process and helps Google crawl your updated page faster.
Step 8: Improve Page Load Speed
Page load speed is crucial for both user experience and SEO. Google rewards fast pages that load quickly, and slow pages may get deprioritized or even deindexed. Here’s how to improve page speed:
- Check Page Speed: Use PageSpeed Insights or similar tools to identify slow-loading pages and their causes.
- Optimize Images and Code: Compress images, minify JavaScript and CSS files, and remove render-blocking resources to improve load times. These optimizations can significantly enhance crawlability and help pages get indexed faster.
Step 9: Ensure Mobile-Friendliness
With Google’s mobile-first indexing, it’s essential that your site is mobile-friendly. Mobile-friendly sites are more likely to be indexed and rank well. Here’s what to do:
- Check Mobile Optimization: Use Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test tool to ensure that your pages are optimized for mobile devices. A mobile-friendly site improves user experience, helping ensure pages remain indexed.
Step 10: Monitor for Spammy or Low-Quality Backlinks
Backlinks play a key role in SEO, but spammy or low-quality backlinks can harm your site’s reputation and result in pages not being indexed by Google. Here’s how to manage backlinks:
- Check Backlink Profile: Use tools like Ahrefs or Google Search Console’s Links Report to monitor your backlinks.
- Disavow Toxic Links: If you find spammy or harmful backlinks, disavow them to prevent penalties and protect your site’s credibility.
Step 11: Submit an Updated Sitemap
An updated sitemap helps Google crawl and index your site more efficiently. If you’ve fixed issues related to pages not indexed by Google, submit an updated sitemap:
- Update and Resubmit Sitemap: After resolving issues, submit an updated XML sitemap in Google Search Console. This helps Google recognize new or updated content and speeds up the reindexing process.
Conclusion
Fixing pages not indexed by Google requires a detailed, multi-step approach. From identifying and addressing technical issues to improving content quality and ensuring mobile optimization, every action you take will help improve your site’s visibility and SEO performance. By regularly monitoring your site’s health and implementing the best SEO practices, you can restore visibility to your pages, ensure they remain indexed, and improve your overall rankings on Google.
FAQs on Pages Not Indexed by Google
What causes pages to be de-indexed by Google?
De-indexing typically happens due to manual actions, security issues, low-quality content, or technical problems like noindex tags and robots.txt restrictions.
How can I check if my page has been de-indexed?
You can use Google Search Console’s Coverage Report to check if your page has been de-indexed and to identify any errors.
Will resubmitting my sitemap help?
Yes, submitting an updated sitemap can help Google re-crawl your site and ensure all important pages are indexed again.
Can ChatGPT or Gemini Help Resolve Indexing Issues?
Yes, both ChatGPT and Gemini can help with indexing issues. Just describe the problem, and they’ll provide suggestions or steps to fix it.
Leave a Reply